In this article, you will learn to write a C++ Program to implement Doubly Linked-List. The doubly linked-list is a linear data structure that allows traversing the list in both direction.
This program is written using Turbo C++ 3.0 compiler installed on a Windows 7 64-bit PC.
Problem Definition
The doubly linked-list structure has two links for each node – previous and next. The previous link points to previous node and next node points to next node to current node. This allows moving through the list in both direction.
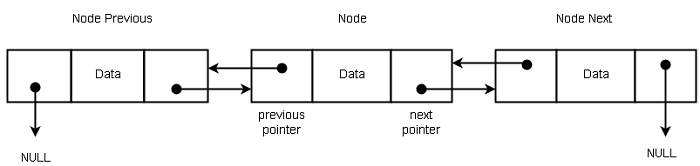
Program Code – Doubly Linked-List
/* C++ Program to Implement a Doubly linked-list
File Name: DoublyLinkedList.cpp
Author: NotesforMSc
*/
#include "iostream.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#include "alloc.h"
#include "conio.h"
//Defining structure of the node
struct Double {
int info;
struct Double *next;
struct Double *previous;
};
//Defining class doubly linked-list
class doubly_link {
public:
int num;
Double start, *temp;
public:
void Doubly_Create(Double *);
void Doubly_Insert(Double *);
void Doubly_Delete(Double *);
void display(Double *);
};
//Function definition for doubly_create()
void doubly_link::Doubly_Create(Double *node) {
start.next = NULL;
start.previous = NULL;
//Start is the first node in the Doubly linked-list
node= &start;
num = 0;
cout << "Input $ to break, else press enter:";
char ch;
ch = getche();
while(ch != '$') {
//Create memory space for next node to start node
node->next = (Double *)malloc (sizeof(Double));
//Point the previous link of next node to start node
node->next->previous = node;
//The next node becomes the start node now
node = node->next;
//Read data value for the node
cout << "\n Input data for node:" << (num + 1) << ":";
cin >> node->info;
//The Next Pointer of the node points to NULL
node->next = NULL;
cout << "Input $ sign to end, else press enter:";
ch = getche();
num++;
}
cout << "\nTotal Nodes =" << num;
}
//Function definition for Doubly_Delete()
void doubly_link::Doubly_Delete(Double *node) {
node = start.next;
if(node == NULL) {
cout << "\n Underflow";
}
else {
//If you want to delete Node, change the
//next pointer of Previous node, point to Next node,
//and change the previous pointer of Next node,
//point to Previous node.
node->previous->next = node->next;
node->next->previous = node->previous;
free(node);
}
}
//Function definition for Doubly_Insert()
void doubly_link::Doubly_Insert(Double *node) {
temp = (Double*)malloc(sizeof(Double));
cout << "\n Insert the node value:";
cin >> temp->info;
node = start.next;
if(node == NULL) {
cout << "\n Node is empty";
}
else {
//The temp node next points to node
temp->next = node;
//The temp node previous points to
//start node next (node->previous)
temp->previous = node->previous;
//Start node (node->previous) next pointer
//points to new temp node
node->previous->next = temp;
}
}
//Function definition for display()
void doubly_link::display(Double *node) {
node = start.next;
do {
cout << "-->";
cout << " " << node->info;
node = node->next;
}while(node != NULL);
getch();
}
//MAIN PROGRAM STARTS HERE
void main() {
doubly_link dlinked_list;
int br;
clrscr();
cout << "\t\t\tDOUBLY LINKED LIST";
cout <<"\n\t\t~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n";
cout << "1-Create List" << endl;
cout << "2-Insert Nodes" << endl;
cout << "3-Delete Nodes" << endl;
cout << "4-Display List" << endl;
cout << "0-Exit" << endl;
cout << "\n";
cout << "Enter Your Choice, 0 to end:";
cin >> br;
while(br != 0) {
switch(br) {
case 1:
Double *node = (Double *)malloc(sizeof(Double));
dlinked_list.Doubly_Create(node);
break;
case 2:
cout << "\nInserted node\n\n";
dlinked_list.Doubly_Insert(node);
break;
case 3:
cout << "\nDeleted node\n\n";
dlinked_list.Doubly_Delete(node);
break;
case 4:
dlinked_list.display(node);
break;
default:
cout << "Sorry ! Wrong Input" << endl;
break;
}
cout << "\n Enter Your Choice, 0 to end:" << endl;
cin >> br;
}
}
Output – Doubly Linked-List
DOUBLY LINKED LIST
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1-Create List
2-Insert Nodes
3-Delete Nodes
4-Display List
0-Exit
Enter Your Choice, 0 to end: 1
Input $ to break, else press enter:
Input data for node: 44
Input $ to break, else press enter:
Input data for node: 88
Input $ to break, else press enter:$
Enter Your Choice, 0 to end: 4
-->44 -->88
Enter Your Choice, 0 to end: 2
Insert the node value : 55
Enter Your Choice, 0 to end: 4
-->55 -->44 -->88
Enter Your Choice, 0 to end: 0