Here is my notes on Extreme programming and Agile process. Agile process model works on action based software development, the practitioners of agile prefer face-to-face communication, daily meeting and active software development approach. They want to build software that is useful and have required components rather than all the fancy unwanted features.
Agile Principles
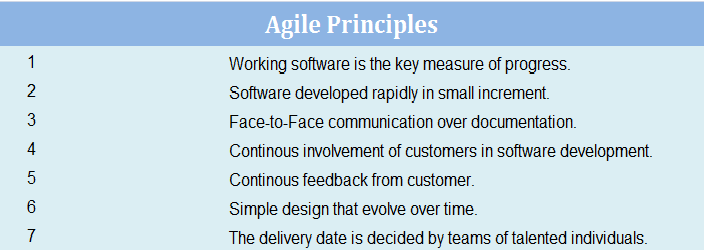
Extreme Programming Philosophy
- Extreme programming starts with user stories, which are scenarios that customer and user would like in the system. Detailed requirements are not mentioned in User Stories.
- XP Team then estimates how long it will take to implement the user scenario.
- Based on the User Stories and Estimates, the release planning is done in advance. That define the user stories built in which release and release dates of this release.
- Frequent release of iteration is employed.
- An acceptance test is also built from these stories bugs found in the iteration, becomes work item for next iteration.
XP and Agile Process
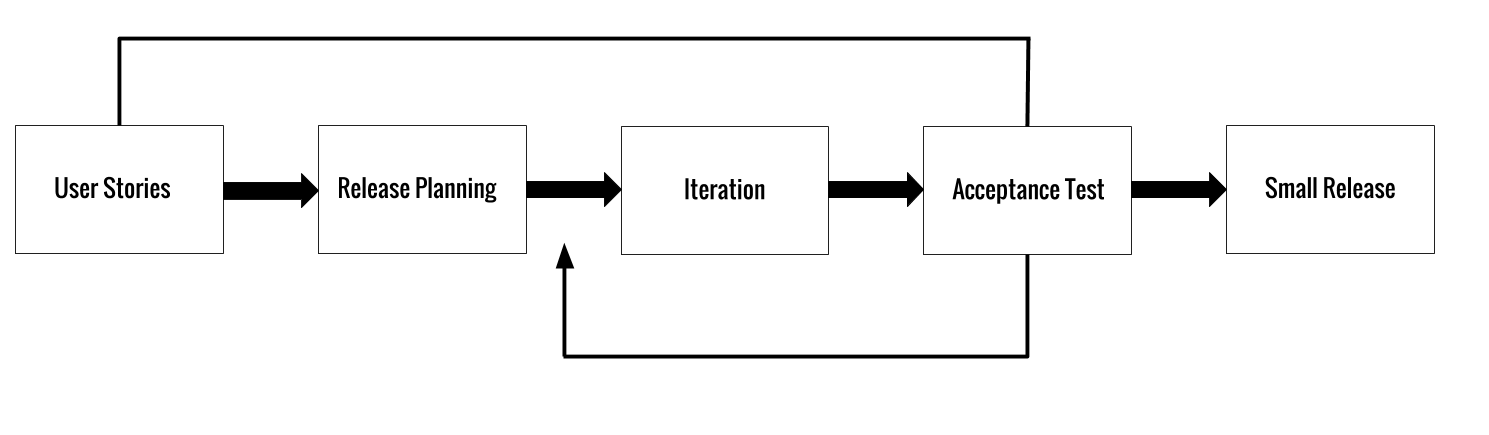
An iteration starts with iteration planning, user stories to implemented in selected high values and high risk are of high priority.

If an iteration failed the acceptance test, then it is included in the next iteration.
Some unique practices of XP programming
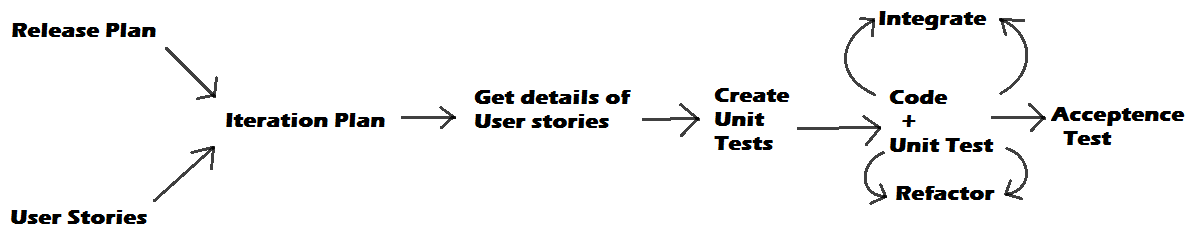
- Programming is done in a pair , not individually.
- A unit test is written first and then actual software code written to pass the test.
- Changes are not made to the obsolete codes, instead, focus on refactoring the codes. All unused functionality is eliminated and what is necessary is built first.
- Keep everything simple.
- At a time, only one pair can integrate into the Base unit.
Other Rules
- Rights of customers and programmer.
- Communication between Team Members, every morning they do a small meeting.
- Decide how meetings should be conducted?
- Spike solutions to resolve technical or architectural problems.