In the previous article, we learned about subroutines. You will learn about VB 6 functions in this article and learn the difference between a function and a subroutine.
A Vb 6 subroutine receives an argument but does not return anything. However, a function takes an argument and returns a value. A VB 6 function is a block of code that can separate your program into manageable parts.
Declaring a VB 6 Function
[Private | Public | Friend] [Static] Function name [(arglist)] [As type]
...
[Statements]
...
[expression]
...
[Exit Function]
...
[Statement]
...
End Function- Public keyword – All procedures in all other modules and forms can access the function.
- Private keyword – All procedures and function in the same module or form where the function is declared can access it.
- Friend keyword – Used only in modules that uses classes and it means that all procedures throughout the project can access this function except the controller of an instance of an object.
- Static – Normally, a local variable to a function get destroyed when function terminates. Static keyword keeps the value of a local variable intact between function calls.
- Function name – User-defined name for the function.
- arglist – A list of variables passed as arguments to the function.
- type – The return data type of the function.
- Statements – A group of statements that a function can execute.
- Exit Function – A way to exit the function immediately before it could complete execution.
- End Function – Terminates the function upon completion.
How to declare arglist in the function?
Arguments to a function are values that the function will use to complete a calculation or complete a task.
To call a function you have to use the function name and the list of arguments which uses the following syntax.
[Optional][ByVal|ByRef][ParamArray] varname[()] [As type][= defaultvalue]Now, we will briefly discuss the list above.
Optional – This keyword means that the arglist is optional and not required.
ByRef – This keyword means that a reference to the original value is passed through the function.This is true by default.
ByVal – This keyword means that the original value of the variable is passed to the function.
ParamArray – Usually you can send limited number of variables through a function, however, if you need to send a list of values of same type use the ParamArray or nothing at all, because this is optional.
varname – It is the programmer-defined name of the argument.
type – This defines the data type of the argument.
defaultvalue – If you want to set a optional default value for a argument, this feature is helpful. If no value is supplied for a variable, then the function can use the default value for computation.
Example Program: VB Function
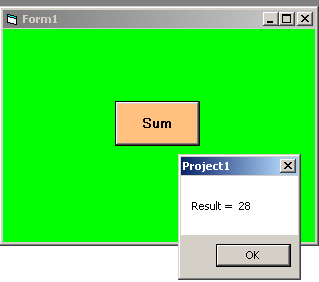
In this example, we will create a simple function that accepts two numbers and return their sum.
VB Code
Private Sub Command1_Click ()
Dim result As Integer
result = Sum (5, 23)
MsgBox ("Result = " + Str(result))
End Sub
Function Sum (number1 As Integer, number2 As Integer) As Integer
Sum = number1 + number2
End FunctionOutput