The Data Definition Language( DDL ) commands are used for creating new or modify existing schema of a relation. You can also set constraints such as key constraints, foreign key constraints, etc on a relation.
CREATE TABLE Command
This command creates a new relation or table. You must specify the fields and data type for each field while using this command.

ALTER TABLE Command
This is most important of DDL commands because it allows us to modify the table anytime.
Here are some examples of ALTER TABLE command
Adding a primary key for the table. A primary key uniquely identifies a tuple in a relation.
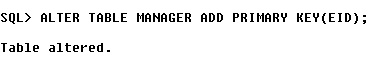
Adding a foreign key for the table. A foreign key in a relation refer to primary key of another relation and cannot be null called the Referential Integrity.
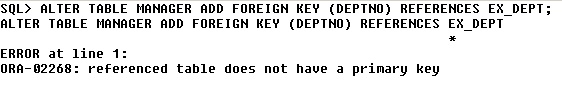
In the above example, we receive an error because the attribute ‘DEPTNO’ is not set as primary key in relation to ‘EX_DEPT’.
After adding ‘DEPTNO’ as primary key we are able to set the foreign key for ‘MANAGER’ relation.

Adding a new column in a Table. In the following example, we are adding ‘PCODE‘ in the ‘MANAGER’ table.

Removing a column from a relation or table. In the following example, we are removing the ‘PCODE’ column from the ‘MANAGER’ table.

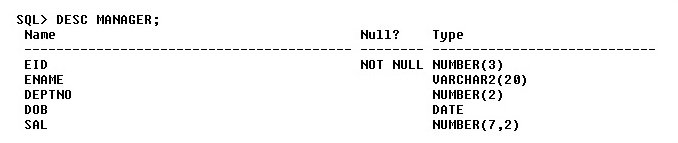
DESC <Table Name>
The ‘DESC’ command helps view the schema of the relation.
DROP TABLE <table name>
This command will drop the table permanently.

References
Avi Silberschatz, Henry F. Korth, and S. Sudarshan. 27-Jan-2010. Database System Concepts. McGraw-Hill Education.
Ramakrishnan, Johannes Gehrke, and Raghu. 1996. Database Management Systems. McGraw Hill Education; Third edition (1 July 2014).
Wikipedia. n.d. Data definition language. Accessed March 14, 2018. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_definition_language.