Computer networks are a form of a data communication system where data refers to information in an agreeable form for parties sharing and using them.
What is Data Communication?
Data communication itself is an exchange of data between two devices over a medium such as a cable wire. The devices that are part of communication must have the necessary hardware and software to complete the communication.
The effectiveness of data communication depends on:
- Delivery
- Accuracy
- Timeliness
- Jitter
Delivery
The data must get delivered to the correct destination.
Accuracy
The data must be accurate when it arrives at the destination device. Inaccurate data is of no use.
Timeliness
There is no use of the data that is delayed. Therefore, it must be delivered in a timely manner.
Jitter
Jitter happens when audio and video arrive at the destination at different time. There is a never delay in delivery of the packets.
What are the important components of data communication?
The data communication involves certain components that work together to complete the communication process. They are:
- Message
- Sender
- Receiver
- Communication Medium
- Protocol
Message
The message is the information that the sender share with the receiver over a communication medium.
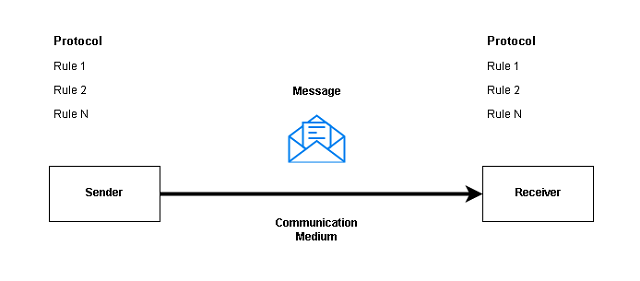
Sender
A sender is the source of the message who is responsible for creating and sending the message to a receiver.
Receiver
A receiver is a destination for the message over a communication medium.
Communication Medium
A communication medium is a link between sender and receiver. Wired and Wireless medium are two types of communication mediums available to us.
Protocol
The protocol is a set of rules for communication. This is one of the most important features of the data communication system. The protocol must be same for both sender and receiver otherwise communication will fail.
How to represent data?
You have learned that the purpose of data communication in a network is to send and receive messages. There are many forms of data available.
- Text
- Images
- Numbers
- Audio
- Video
Text
The text is the most common method of sharing information. A message in text form could be email, chat, or a webpage, or a word processor file. Textual information is made of ASCII alphabet characters or uses UTF-8 characters.
Images
The images are visual information. It could be a digital photograph, vector, or any illustration. Images are displayed in computers in pixels or line drawings. The pixel decides the resolution of the image, if a sender sends a higher resolution image, the receiver must have the ability to show the same resolution, otherwise, the most suitable resolution is selected for the image.
Numbers
The numbers are ANSII characters that start from 0 to 9. The numbers are important to represent numeric information such as financial data or some statistics.
Audio
Audio is broadcasted over the network or sent as a recorded message to receivers. Audio files are of many forms such as mp3, aac, etc. These files could be listened to with any audio player.
Audio information can be broadcasted over a wireless or wired medium to more than one receiver. For example, radio is a very popular medium, telephones are a common audio device to speak directly.
Video
A video is moving visual information. Unlike images, the video is recorded and sent or broadcasted like audio over a network. The computer saves video information in the form of mp4, MPEG, mkv, etc files.
Data flow in Communication
The data communication between the sender and the receiver has direction in some communication systems. They are:
- Simplex
- Half-Duplex
- Full-Duplex
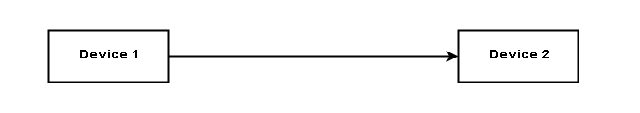
Simplex
In the simplex type, data communication happens only one direction. For example, the radio broadcast where the receiver can only listen to the audio.
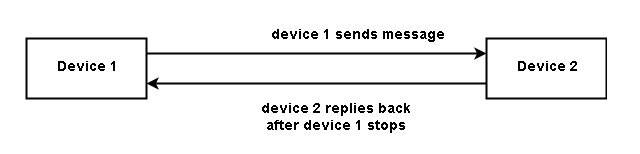
Half-Duplex
The half-duplex is two-way communication with data flowing in either direction at a time. Walkie-Talkie communication is a half-duplex communication with one person talking on either side at a time.
Full Duplex
The full duplex communication gives the ability to communicate two way all the time. All modern communication devices have this ability.

For example, a mobile phone is a popular medium of communication.