A topology is the physical structure of the network using different types of connection. In this article, you will learn about network topologies such as mesh, star, ring, and bus topology.
A network is two or more devices connected through links where the link transfers data from one device to another.
The link connects the devices and they are of two types:
Point-to-point connection
This type of connection has a dedicated link between two devices. The devices use the entire capacity of the link.
Example,
TV remote control use infrared to control TV.

Multipoint or Multidrop connection
More than two devices are connected to the link. The capacity of the link is either spatially shared(simultaneously connected) or time-shared (take a turn to use the link).
Network Topologies
A network topology defines the physical structure of the network. Here is a list of network topologies.
1. Mesh
2. Star
3. Bus
4. Ring
5. Hybrid
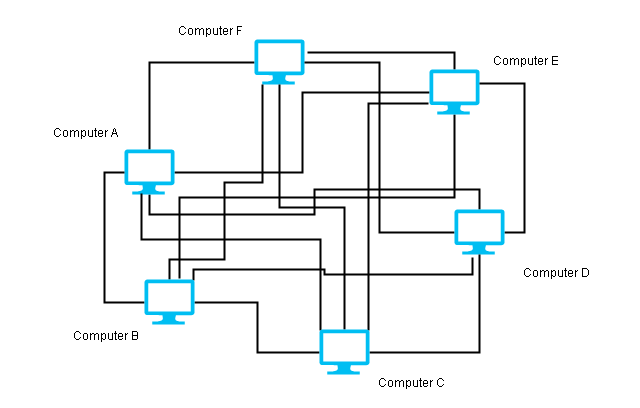
Mesh Topology
The mesh topology consists of a point-to-point connection between every device using a dedicated link. If there are n nodes in the network, then it makes n (n-1) / 2 duplex links.
Advantages
- If one link fails in a mesh that will not cause the whole network failure. Only that link is affected.
- The point-to-point connection makes fault identification easier and ensures the proper delivery of the packets.
Disadvantages
- The mesh network uses too many ports that make it expensive.
- Too many cables make it difficult to implement this network, therefore, a mesh is only required when the network is closed or requires high availability. Example, telephone regional offices are connected through the mesh.
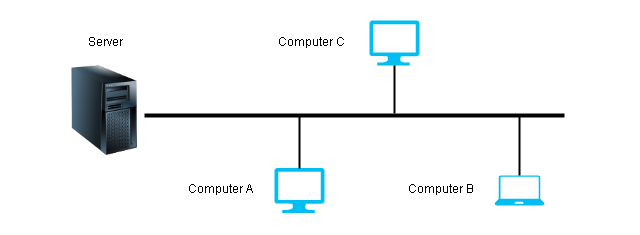
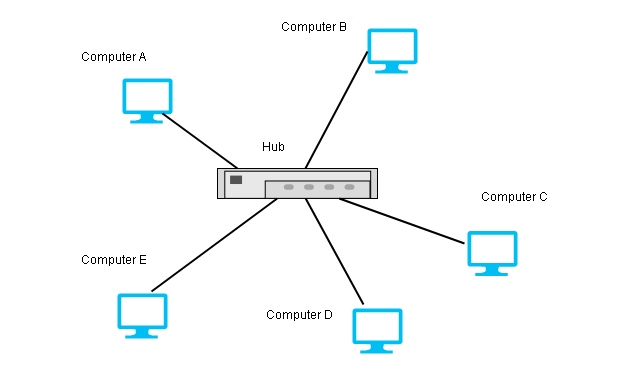
Star Topology
The star topology makes a point-to-point connection to a hub device. The hub exchange data on behalf of the devices.
Advantages
The star topology is not expensive because of less number of cables and ports required as compared to mesh.
A failure of one link in star topology does not fail the whole network. Only that link is failed.
The number of ports on devices is also less as compared with a mesh topology.
Disadvantage
If the hub device goes down or becomes faulty, the entire network goes down.
Example,
This type of topology is used in LAN (Local Area Network).
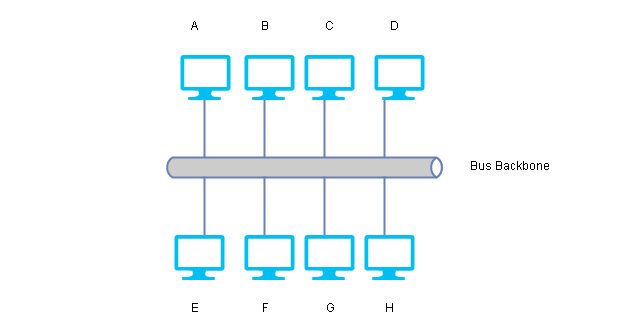
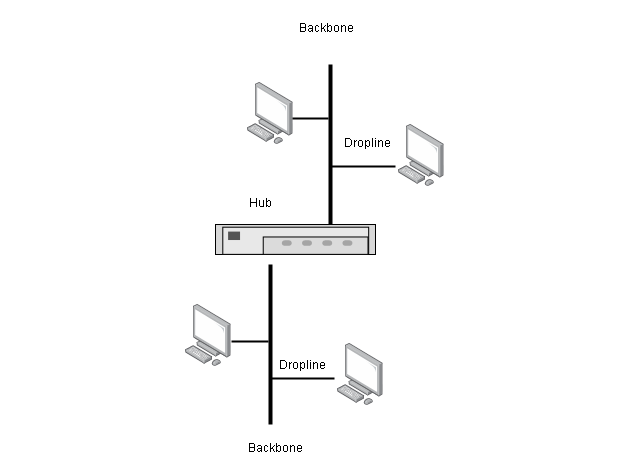
Bus Topology
The bus topology uses a multipoint connection, and all devices are connected to a backbone link in the network. The backbone is one long cable to which nodes are connected using droplines and taps. A dropline is a connection between the device and the backbone. A Tap is a connector that creates contact with the metallic core of the backbone.
Advantages
- A bus topology is easy to install. It uses less cabling because only backbone and droplines are required.
- A new device installation requires changing backbone because it may not be of sufficient length.
Disadvantages
- The backbone signals become weaker and weaker towards the other end of the cable as it travels some distance.
- There is a limit to the number of devices a bus topology can support due to backbone capacity.
- Failure at any point in the network can cause complete failure of the network.
- Fault isolation is difficult.
Example, early LANs were bus topology networks.
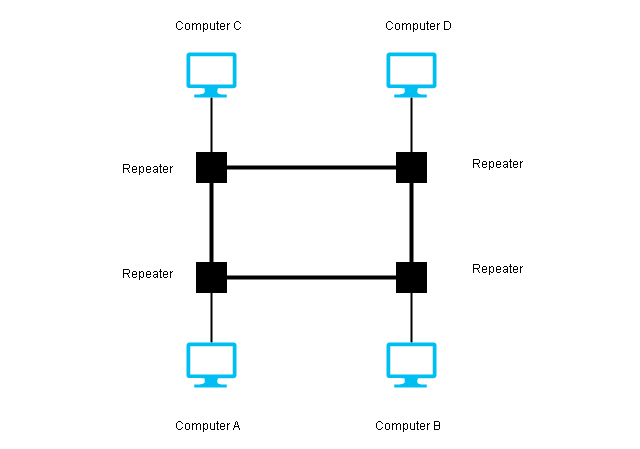
Ring Topology
A ring topology appears like a ring where a single device is connected using point-to-point on either side. A single pass from one direction in the ring until it reaches its destination.
Each device has a repeater, if the message intended for another device, then the repeater regenrates it and passes it to the next device. Otherwise, it accepts it.
Advantages
- Easy installation and fewer cables.
- In a ring topology, fault isolation is easy. When a repeater not working an alarm can alert a network administrator with a location.
- Adding new device is easy because you only need two connections on either side of the device.
Disadvantages
- The only difficulty with ring topology is that a single device failure can cause the whole network to go down.
Hybrid Topology
A hybrid topology is made of a combination of two or more network topologies.
Consider the above example, star topology and each connection of star can be a bus network.