The Relational Database Management Systems is the most popular database system. The overall structure of the Database System is given here. The relational database is at three level or three schemas.
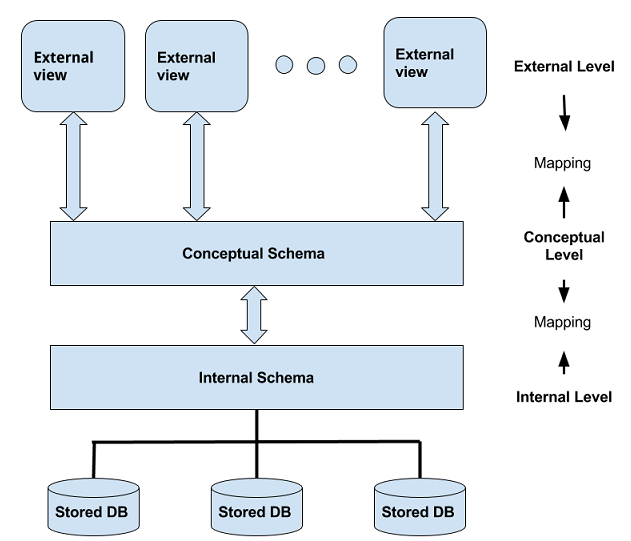
Internal level with internal schema
In this level, an internal schema is defined and it is more related to the physical storage and access path of the database,
Conceptual level with conceptual schema
This level describes the structure of the database and describes what entities, data types, constraints and user operations defined on the database. You can also call it in memory DBMS.
Data Definition Language is used for defining this schema. Here are some examples of DDL commands.
- ALTER
- DROP
- CREATE
External or View level with number of External Schema or Views
At this level, you will get only part of the database as users and the rest of the information is hidden. This is implemented using the representational data model which is easily understood by the users.
Database Terminology
There are some important terminologies about a database that you should know. Data in a database at a particular instance is called the Database State or Snapshot. Whenever, we insert, delete and update any data, we change the database state.
The description of database and constraints are stored in a file called Metadata. You can also call it data about data. For example, if a database field “Name” store names of people, then Metadata will describe the data type for this field as “Char”, means this field will only contain strings of characters and so on.
An Access path is a structure, that will make access to data or search for data more efficient. An Index is a file that will provide direct and fast access to data record using some keywords or search terms. The Index is similar to an index of a book which contains some keywords for reference.
Bibliography
Avi Silberschatz, Henry F. Korth, and S. Sudarshan. 27-Jan-2010. Database System Concepts. McGraw-Hill Education.
Ramakrishnan, Johannes Gehrke, and Raghu. 1996. Database Management Systems. McGraw Hill Education; Third edition (1 July 2014).