In this article, we will evaluate operational database vs. data warehouse. Operational database is live database which uses normalization, concurrency control to manage transactions, and have a recovery mechanism. It is used by OLTP (Online Transaction Processing) applications.
The data warehouse is kept separate from the OLTP databases. It is used by the OLAP( online analytical processing) applications. It is more about summarization and aggregation of data. If applied to a operational database, it will slow down the OLTP system.
Difference Between Operational Database and Data Warehouse
When we say operational database, we actually mean OLTP systems, and data warehouse means OLAP systems. Therefore, in the following table, you find feature-wise comparison of these two databases.
| Features | Operational Database | Data warehouse |
| Users | Clients, Clerks, IT guys | Managers, Executives, Analysts |
| System Orientation | Customer oriented, data-to-day operation | Market Oriented, Decision support |
| Data | Current data | Historical data |
| DB Design | E-R Model | Star or Snow flake Model |
| View | Focus on current data, same organization | Focus on multiple versions of data, heterogeneous sources |
| Volume | Not very large | Huge, stored in many disks |
| DB Access | Short, atomic transaction, ACID property | Read-only access with complex queries |
| Operations | Index/Hash on Primary key | Lot of Scans |
| No. of records | Tens | Millions |
| DB Size | 100 MB to GB | 100 GB to TB |
| Priority | High priority | High flexibility |
| Metric | Transaction throughput | Query response time |
Multi-Dimensional Data Model of Data Warehouse
A multi-dimensional model categories data as
- either facts with numeric measures.
- or as dimensions that characterize the facts and are mostly textual.
For example.
Product sold to customer in certain amount and price
Fact : – purchase
Measures:- amount, price
Dimension:- location, type of product, time of purchase
Multi-Dimensional Model
Multi-dimensional data model is composed of logical cubes, measures, dimensions.
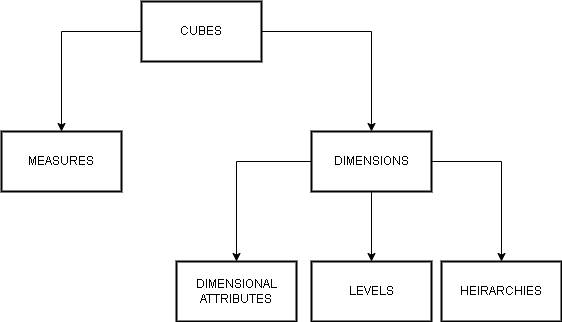
Measures – It populate the individual cells of a logical cube.
e.g. quantity of sales which is some number
Dimension – They are ways to look at the measures. A cube has 3 dimensions. Each of the dimension has cells with some quantity as measures. One dimension may be location,another time, and so on.
Logical hierarchies – They are ways to organize data at different level of aggregation. The members at each level have one-to-many and parent-child relationship.
e.g Quarter-I ( year 2018), Quarter-II (year 2018), Quarter-III(year 2018)
The quarter-i, quarter-ii, and quarter-iii are children of year 2018.
e.g Year -> Month -> Weeks -> Days -> Hours (5 levels)
Sales Target ->Area -> Sales Rep -> Individual Target (4 levels)
The hierarchy and levels have many-to-many relationship.
Logical Attributes – It provide additional information about the data.
Multi-Dimensional Data Storage
The data cube represents all measures. Each dimension is the edge of the cube. They divide the cube into cells containing values or data.
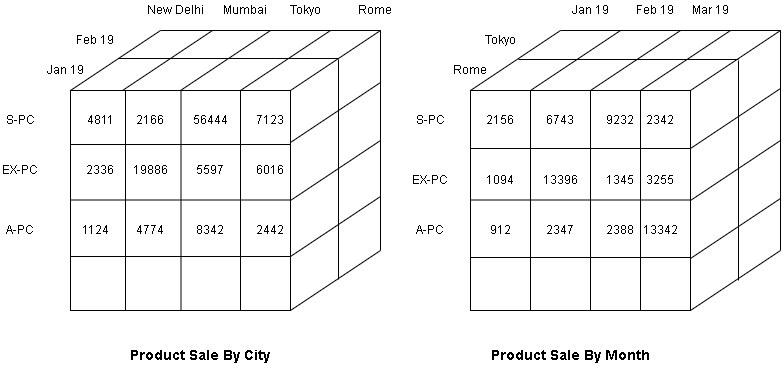
The cube can rotate to give many view of same data. It also represents physical storage of measures, just like relations in OLTP database.
A measure can have more than three dimensions, but pictorially, cube has only 3 dimensions and additional dimensions requires additional cubes.
Schema For Multi-Dimensional Database
The relational implementation of the multi-dimensional data model is a
- A Star Schema
- A Snowflake Schema
- A Fact Constellation Schema
We will discuss the architecture of data warehouse in future lessons. In this article, you learned that the data warehouse is different in all aspects compared to operational database.