The ![]() loop is a simpler version of the while loop that we learned in the previous lesson. It has the same components as while loop.
loop is a simpler version of the while loop that we learned in the previous lesson. It has the same components as while loop.
For Loop Basics
The for loop is more popular because all conditions for loop is declared in one place.
Before the for loop starts.
- Loop variable – It is used for initializing the loop, test condition for loop and increment or decrement the loop.
- Loop test condition– decide whether to execute the loop body or not.
- Loop body – contains statements required for performing a task inside the loop.
Logically ![]() loop and
loop and ![]() loop is same but the
loop is same but the ![]() loop is lot more simple than the
loop is lot more simple than the ![]() loop. This is because you can initialize, put test conditions and increment or decrement the
loop. This is because you can initialize, put test conditions and increment or decrement the ![]() loop in a single line.
loop in a single line.
for( initialize counter; test condition; increment or decrement counter)
{
Statements;
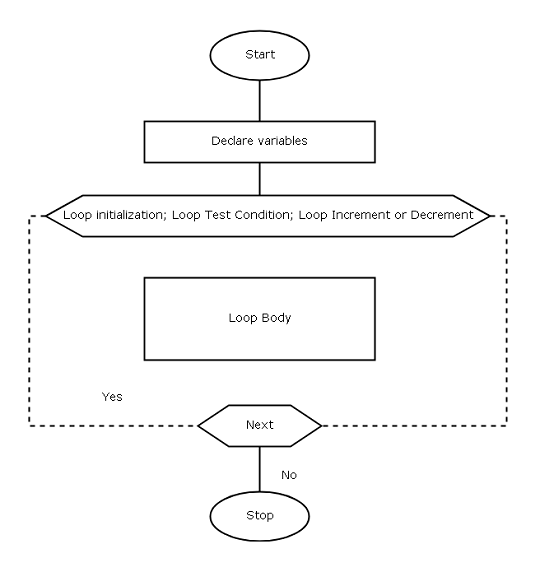
}Flowchart Symbol of ‘for’ loop
The following symbol is used when we draw a flowchart for a C program that make use of a ![]() loop.
loop.
Example Program
In this example program, we are going to a number over and over for 10 times and print the result. This program uses a single ![]() loop.
loop.
Your site doesn’t include support for the CodeMirror Blocks block. You can try installing the block, convert it to a Custom HTML block, or remove it entirely.
Install CodeMirror Blocks
Keep as HTML
/* C Program to add a number 10 times */
#include <stdio.h>
int main ()
{
int number, total, i;
number = 2;
total = 0;
for (i=0; i<10; i++)
{
total = total + number;
}
printf ("\n\n\n\n");
printf ("\t\t\tThe total is %d", total);
getch ();
return 0;
}Output
The total is 20Example Explained
The program has three variables – loop variable ![]() and
and ![]() and it uses one
and it uses one ![]() loop to repeatedly add the number to
loop to repeatedly add the number to ![]() until the loop terminates.
until the loop terminates.
First the variables ![]() and
and ![]() are initialized.
are initialized.
total = 0;
number = 2;The loop variable ![]() is used inside the
is used inside the ![]() loop to initialize the loop, define the test condition and increment the loop.
loop to initialize the loop, define the test condition and increment the loop.
for (i =0; i<10; i++)Since the loop starts at ![]() , it will run for 10 iteration because the 10th iteration it will terminate. At each iteration, the loop will check the test condition against the current value of
, it will run for 10 iteration because the 10th iteration it will terminate. At each iteration, the loop will check the test condition against the current value of ![]() .
.
When the condition for loop is ‘true’, the loop body will execute and add value of variable ![]() to
to ![]() repeatedly.
repeatedly.
total = total + number;The loop adds the ![]() 10 times and when
10 times and when ![]() , it terminates and prints the value of
, it terminates and prints the value of ![]() as output.
as output.
printf ("\t\t\t\t The total is %d", total);The program ends.
References
- Balagurusamy, E. 2000. Programming in ANSI C. Tata McGraw-Hill Education,.
- Kanetkar, Yashavant. 20 November 2002. Let us C. Bpb Publications.