We know that the simple statements are represented as p, q and so on. Suppose we are given a compound preposition.
There is another property of compound prepositions called the duality; Therefore, the dual of above statement is
The dual can be achieved by interchanging by
or interchanging
by
. This means
and
is dual of each other.
Dual For Another Type Of Statement
We will see an example of another type of prepositional statement in which we use True or False directly instead of a variable.
For example,
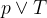 is a preposition with T or True as one of the variable.
is a preposition with T or True as one of the variable.The dual of such a statement can be obtained by interchanging by
and interchanging True with False or False with True.
Each of the statement can be derived from the other.
Understanding Duality Using Truth Tables
These are the truth tables for the statements – and
.
| T | T | T |
| T | F | F |
| F | T | F |
| F | F | F |
| T | T | T |
| T | F | T |
| F | T | T |
| F | F | F |
If we change the operator for with
, or vice-versa, we get dual of each other. The truth table validates this claim. We can check this for other prepositional statements also.