In python programming, you can run a specific block of code with the help of conditions. Usually, these types of block start with ![]() statement.
statement.
The ![]() statement in python can change the direction of the program with these conditions. Suppose condition is true, then
statement in python can change the direction of the program with these conditions. Suppose condition is true, then ![]() will be executed and if condition is false, then nothing happens. The program continues with the rest of the statements. See the figure below
will be executed and if condition is false, then nothing happens. The program continues with the rest of the statements. See the figure below
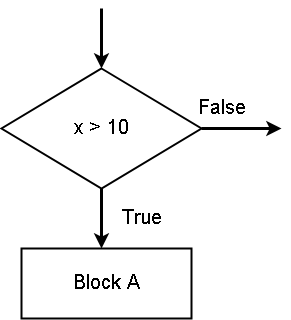
In the figure above, if the condition ![]() is true, the python executes the
is true, the python executes the ![]() statements. If the condition is false, nothing happens.
statements. If the condition is false, nothing happens.
Example – if block
In this example, we will check if a customer has enough cash to buy a product whose price and tax if given. If the customer has enough cash, then he can buy the product, otherwise, purchase cannot be made.
# Customer declare the amount of cash
cash_available = 5000
# Price of the item is 3000 and tax amount is 100.
price = 3000
tax = 100
# Now we check if cash is less than total of price and tax, so that we can # decide the purchase
if cash <= price + tax:
total_amount = price + tax
print("Purchase Successful", total_amount)
print("Transaction Completed")In the program above, observe how ![]() statement ends with a
statement ends with a ![]() . Also, watch each line start with an
. Also, watch each line start with an ![]() and not with a
and not with a ![]() . The semi-colon is a way to tell the program that a new block is starting after the
. The semi-colon is a way to tell the program that a new block is starting after the ![]() statement. Statements inside a single block must have the same indentation rules.
statement. Statements inside a single block must have the same indentation rules.
Output – if Block
The output of the above program is as follows.
Purchase Successful 3100 Transaction Completed