In previous two articles, we discussed conditional statements such as ![]() and
and ![]() . All of those previous structures are using one conditions only, what if, we want to check multiple conditions at different time and make decisions based on the output of those conditions. The python has a special
. All of those previous structures are using one conditions only, what if, we want to check multiple conditions at different time and make decisions based on the output of those conditions. The python has a special ![]() construct to check multiple conditions one after another. Look at the figure below to understand this logic better.
construct to check multiple conditions one after another. Look at the figure below to understand this logic better.
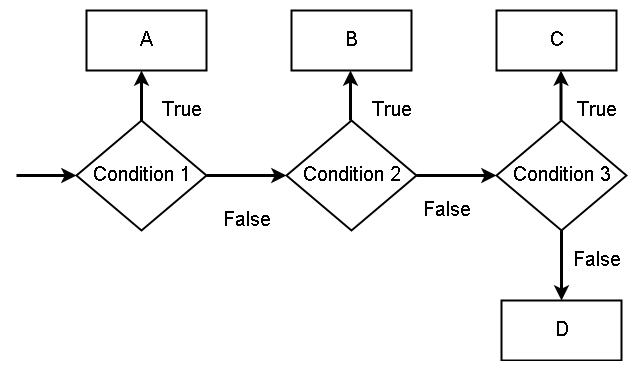
Note that the condition 1 comes from if-block, condition 2 comes from elif, condition 3 is elif and else block is D.
The first condition, ![]() is the if-block and if true then executes the
is the if-block and if true then executes the ![]() and if false will move to the next condition, which is
and if false will move to the next condition, which is ![]() . If
. If ![]() is true, that will execute
is true, that will execute ![]() and if it is false then move to
and if it is false then move to ![]() . The
. The ![]() if true will execute the
if true will execute the ![]() and if everything is false, the final output is
and if everything is false, the final output is ![]() .
.
Example – If-then-elif-else
In this example, student receive his grade in ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
\begin{aligned}
&A = Excellent\\
&B = Outstanding\\
&C = Very \hspace{3px}Good\\
&D = Good\\
&E = Fair \\
&F = Fail
\end{aligned}We need to print the result based on the grade that the student gets. Consider the following code.
grade = input("Enter Your Grade:" )
if grade == "A":
print("You grade is Excellent!")
elif grade == "B":
print("Your grade is Outstanding!")
elif grade == "C":
print("Your grade is Very Good!")
elif grade == "D":
print("Your grade is Good!")
elif grade == "E":
print("Your grade is Fair..Work Hard!")
elif grade =="F":
print("Your Failed.. Try again later")
else:
print("Wrong Input")
The output of the program is given below.
Output – If-then-elif-else
=========== RESTART: C:/Python_projects/Display_Student_Result.py =========== Enter Your Grade:D Your grade is Good! >>>