The K-map or Karnaugh map is a graphical tool to minimize a boolean function. From the previous article, you know how a boolean function represented in canonical sum of product is changed into sum of product form using K-map. Also, the k-map is nothing but the same truth table in a matrix form where each of the cell is a minterm.
In this post, you will learn about a 3-variable with an example.
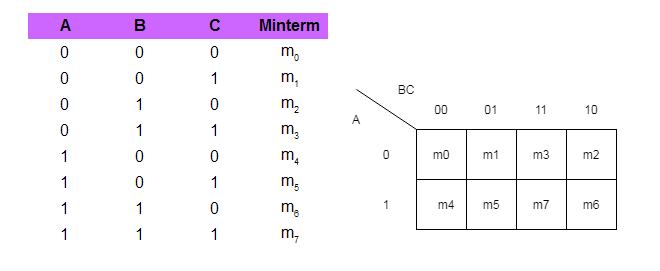
Truth Table for 3-Variable Map
It is a well-known fact that K-map is nothing but a different representation of truth table; therefore, a truth table for 3 variables will contain ![]() rows. This also means that the K-map would contain total of 8 cells, each for a row in the truth table.
rows. This also means that the K-map would contain total of 8 cells, each for a row in the truth table.
Consider the following truth table for three variables – A, B, and C.
Let us understand the characteristics of the 3-variable K-map because it is very important to understand and use this map for boolean function minimization.
Characteristics of a 3-variable K-map
- The truth table has total of 8 rows which corresponds to 8 cells of the 3-variable K-map.
- Each cell differs in only one variable to its neighbor, both horizontally and vertically.
- To minimize the terms in a boolean function, mark a cell as 1 if its output is 1 in the truth table and leave the rest as it is.
- To minimize the variables within each term of a cell that has 1 in K-map, start making groups of 2, 4, and 8.
- Grouping of 1s includes neighboring cells, corners and sides even though they overlap each other.
- Make larger groups if possible.
- Once all 1s are covered then you can stop.
Now that you know the 3-variable map and its characteristics. It is time to see an example.
3-Variable Map Examples
In this section, you will find examples of 3-variable map. These are some examples, you may refer to some textbooks for more examples and practice yourself.
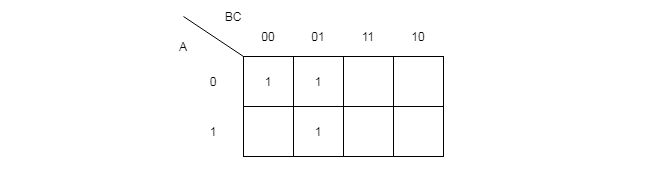
Q1 – Plot a 3-variable map for the following function.
F = A'B'C' + A'B'C + AB'C Solution:
The function use three minterms that gives output 1 as per truth table.
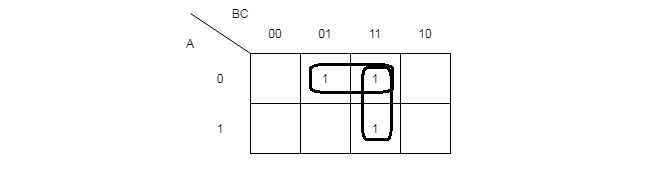
Q2 – Plot a three variable map and show grouping of two for marked cells for the following function.
F = A'B'C + A'BC + ABCSolution:
Q3 – Plot a three-variable map for following function and make group of four cells that are marked as 1s.
F = A'B'C' + A'BC' + AB'C' + ABC'Solution:
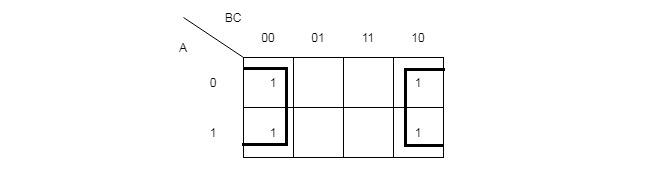
You should note that both sides are overlapped and made into a group of 4 four because two side when compared have a difference of 1 variable, for example, A’B’C’ and A’BC’ has only difference of B’ and B. This applies to both – horizontal and vertical directions. The sides and corners are also neighbors of each other with a difference of 1 variable change.
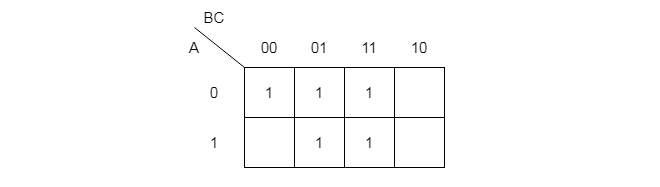
Q4 – Minimize the following Boolean function using K-Map.
F = A'B'C' + A'B'C + A'BC + AB'C + ABC'Solution:
We will find the solution to this problem in step by step manner.
Step 1: Plot a 3-variable map and mark the terms from the function to 1.
Step 2: Make groups of 2, 4, or 8 and only take variables that are common in the group both horizontally and vertically.
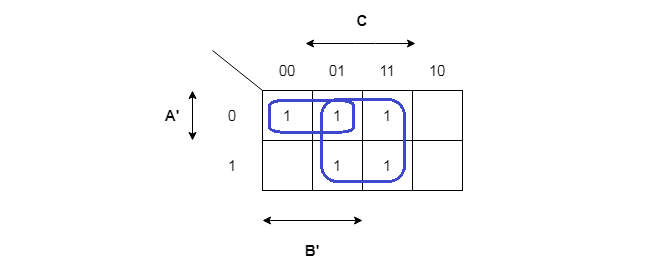
Once you have grouped all the cells with 1s into group of 2s, 4s, or 8s. List all the variables that are common vertically and horizontally. For example
//Group of two
= A'B'C' + A'B'C
= A' is common vertically
= B' is common horizontally
Our first term is A'B'.
//Group of four
= A'B'C + A'BC + AB'C + ABC
= A' + A cancel out vertically, leaving B'C + BC
= C is only common variable horizontally.
Our second term is C.
The final minimized equation is F = A'B'+ CRules for grouping in 3-variable map
- A single cell with 1 gives 3 literals.
- Two adjacent cell group gives 2 literals.
- Four cells with 1s will give a single literal.
In the next article, we will see how to minimize a Boolean function with 4-variable map which has 16 cells to work with.