Earlier you learned about C++ program structure. In this article, you will learn to write about your first C++ program and program elements in detail.
The meat of the C++ is in main function, and before main we need to declare the header files.
Simple C++ Program
Let us consider an example program and then we discuss the program elements in detail. The program declare a header file required for standard input and output operations called ![]() .
.
#include <iostream.h>
void main(void)
{
//Variable declaration
int number;
// Reading input values
cout << "Enter the a number:" ;
cin >> number;
// if block
if (number > 100)
{
cout << "Number is greater than 100;
}
}The above program prints only when the number is greater than ![]() . That is, when the user input a number that is more than
. That is, when the user input a number that is more than ![]() .
.
Variable Declaration
The main program begins with variable declaration. In C++ , you must declare your variable first and the syntax to declare the variable is:
<date_type> <indentifier 1>, <identifier 2>, ... <identifier N>;For example,
int A; // variable declared as integer type
char ID1, ID2,ID3; // variable declared as character type
float Number; // variable declared as floating typeStatements
A statement in C++ program perform some action. Every statement ends with a semi colon (![]() ). The C++ statements can be divided into following category.
). The C++ statements can be divided into following category.
- Simple statements
- Expressions
- Statement blocks
Simple Statements – This type of statement are instruction to get input, print output or any one line statement that ends with a semi-colon.
For example,
cout<< " Hello World ! ";
int number;Sometimes a simple expression can also be a simple statement.
Expressions – An expression is a mathematical expression or an assignment that evaluates to a single value and ends with semi-colon. This type of statements use C++ operators.
For example,
result = number1 + number2;
area_of_triangle = ( 1/2 * base) * height;We can write any type of complex expressions which depends on the problem we are solving.
Statement blocks – In the above program, if block is an example of statement block which encloses many simple statements.
{
if ( x == 0)
{
area = 0;
}
else
{
area = x * x;
}
cout << "Area = " << " " << area ;
}For example,
The example above has two blocks – if block and else block. The if block contains only one statement – an expession and the else block contains two statements.
This the advantage of grouping the statements into blocks, so that you can execute then as part of a task. The else block above computes the area and prints the result. Two actions were performed within a block.
Comments
C++ comments are lines ignored by the compiler. The compiler understands that the comments are not to be executed. The comments are of two types
- Single line comment (
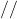 )
) - Multiline comment (
 )
)
Single Line Comment – You can write a single line of text as comment after (![]() ) symbol. See the program above.
) symbol. See the program above.
For example,
// this is a comment ignored by the compiler
// this is another lineMultiline Comment – Inherited from C language, C++ allows to add multiple lines as comments. Anything in between ![]() and
and ![]() is ignored. The multiple line comment is used for describing the program details. There is not restriction on white space or new line for multiline comments.
is ignored. The multiple line comment is used for describing the program details. There is not restriction on white space or new line for multiline comments.
For example,
/*
Program Name: Tax Calculator
Program Author: Notesformsc.org
Program Description: The program receives inputs such as yearly income, tax rates and computes total tax payable by the employees.
Version: 1.0
*/Common Mistakes While Writing C++ Programs
These are some common mistakes by beginners of C++ programming language.
- Forget to add necessary header files.
- Spelling mistakes
- Not initializing the variables
- Not following a naming convention for variables.
- Forget to add semi-colon at the end of the statement.
- Block is not closed.
If you avoid the above mistakes, then you will have a clean and error free programs.
