In the previous article, you have learned about the if-then-else statements and how you can build a program in VB 6 that work on conditions. The problem with if-then-else structure is that it is very difficult to keep a track of all codes.
The Select-Case is a VB 6 feature that allows to select a case when the condition is met and execute a code. It is a more simplified version of if-then-else statements.
Syntax: Select-Case
The syntax for Select-Case is given below.
Select Case expression
Case 1:
some expression;
Case 2:
some expression;
Case 3:
some expression;
Case 4 To 8:
some expression;
Case Is <= Total:
some expression;
Case Else:
some default expression;
End SelectSelect Case ‘expression‘ – Here the Select Case wants a variable or an expression to check if any Case match with it. If there is a match then execute codes under that case.
Case ‘value’ – A case has a number or expression that evaluates to a number. The code under case is executed when the Select Case condition is met.and its value match with the Case value.
End Select – This terminates the Select Case block.
The Case
Each of the case has a value associated with it. It may be in the form of number, or an expression.Let us see few examples below:
Case with number
Case 4: //Case with number and a colonCase with range of values (expression)
Case 4 To 10: // Gives option to choose number between 4 and 10Case with logic (expression)
Case Is >= 20: //Case condition evaluates to true, and code gets executedWhen the case does not match, the last case is Case Else which executes the default statement.
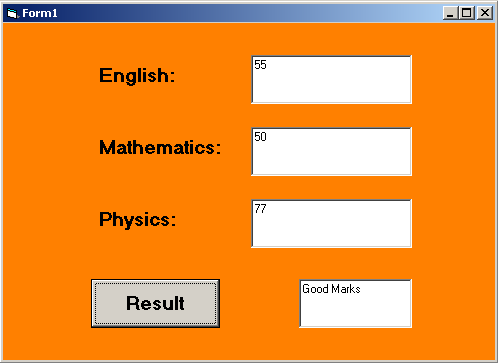
Example Program: Calculator
Private Sub Command1_Click()
Dim physics_mark As Integer, maths_mark As Integer
Dim english_mark As Integer, average As Integer
Dim result As String
physics_mark = Val(Text3.Text)
maths_mark = Val(Text2.Text)
english_mark = Val(Text1.Text)
average = (physics_mark + maths_mark + english_mark) / 3
Select Case average
Case Is <= 50:
Text4.Text = "You Passed"
Case Is <= 70:
Text4.Text = "Good Marks"
Case Is <= 90:
Text4.Text = "Top Student"
Case Is < 100:
Text4.Text = "Exceptional"
Case Else
Text4.Text = "Sorry! You Failed"
End Select
End SubIn the above program, students enter marks for 3 subjects – English, Mathematics, and Physics. The average of the marks is computed and using Select-Case the appropriate result is displayed.
Output – Select-Case