In this article, you will learn about a special function called polynomial function. You can think of polynomials as an expression made of variables, exponents, and constants. Here the number of terms are important, hence, the name “Poly” which means “many” and “nomial” means “terms”.
Standard Form
The standard form of polynomial function is in following form.
\begin{aligned}
&f(x) = a_nx^n + a_{n-1}x^{n-1} + ... + a_2x^2 + a_1x + a_0\\ \\
&where\\\\
&;a \neq 0, n \geq 0 \hspace{2 mm} and \hspace{2 mm} \{ a_n, a_{n-1}, ... , a_2, a_1, a_0 \} \in R
\end{aligned}The value ![]() is non-negative integer and it is called the degree of polynomial function. The value
is non-negative integer and it is called the degree of polynomial function. The value ![]() is leading coefficient for variable
is leading coefficient for variable ![]() with highest power, that is,
with highest power, that is, ![]() . Finally, all coefficients are real numbers.
. Finally, all coefficients are real numbers.
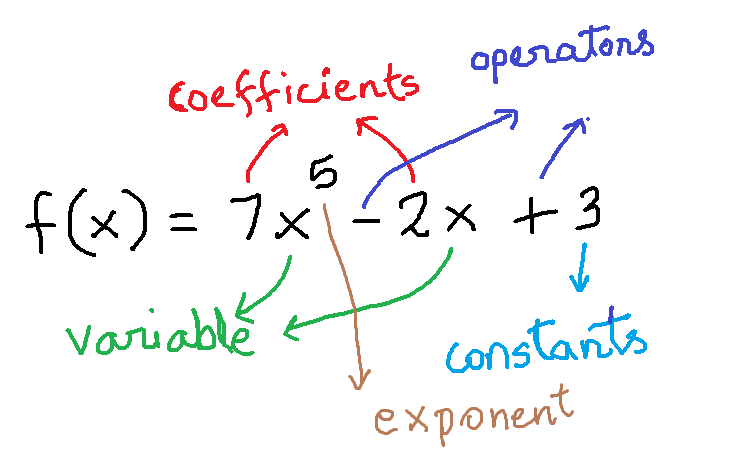
What Is Not Polynomial Function ?
As we mentioned earlier, the coefficients can be any real number, however, the exponents value must be a non-negative integer.
Example #1
![]()
The function ![]() is a polynomial of degree
is a polynomial of degree ![]() because the variable
because the variable ![]() has non-negative integer exponent and the coefficients are real numbers. The negative numbers and radicals are also real numbers.
has non-negative integer exponent and the coefficients are real numbers. The negative numbers and radicals are also real numbers.
Example #2
![]()
The function ![]() is not a polynomial function because it has a fraction exponent, it must be a non-negative integer exponent.
is not a polynomial function because it has a fraction exponent, it must be a non-negative integer exponent.
Example #3
![]()
The exponent in the leading term has a negative value, all exponent in polynomial must be greater than or equal to 0, meaning a non-negative integer.
Polynomial Types Based on Number Of Terms
The terms of polynomial are separated by arithmetic operators such as plus (+) and minus (-). Based on number of terms a polynomial can be classified into:
- Monomial
- Binomial
- Trinomial
Monomial
A monomial is a single term polynomial. A single term can be a constant or a term with variable.
Example #4
![]() where
where ![]() .
.
Note that the variable ![]() is
is ![]() therefore,
therefore, ![]() , and it is also known as constant polynomial.
, and it is also known as constant polynomial.
Example #5
![]() where
where ![]() .
.
Binomial
If the polynomial has only two terms, then it is known as a binomial.
Example #6
![]() where
where ![]() .
.
The above is example of binomial polynomial, but the degree is one. Such a polynomial is called linear function.
Trinomial
The trinomials have three terms.
Example #7
![]() where
where ![]()
These type of polynomial are trinomials and a trinomial with degree two is called a quadratic equation. You can read previous article to know more about quadratic functions.
Graph Of Polynomial Functions
The graph of polynomial function has two characteristic:
- The graph is continuous, meaning it has no breaks.
- The graph is smooth, meaning the graph is a single function with out sharp edge.
A continuous function can be a piecewise function which is not graph of polynomial.
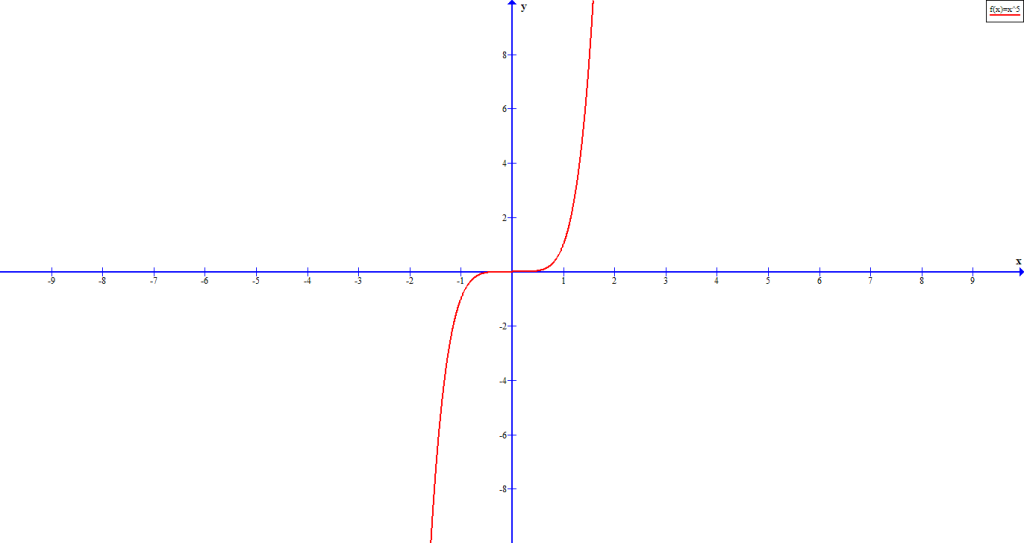
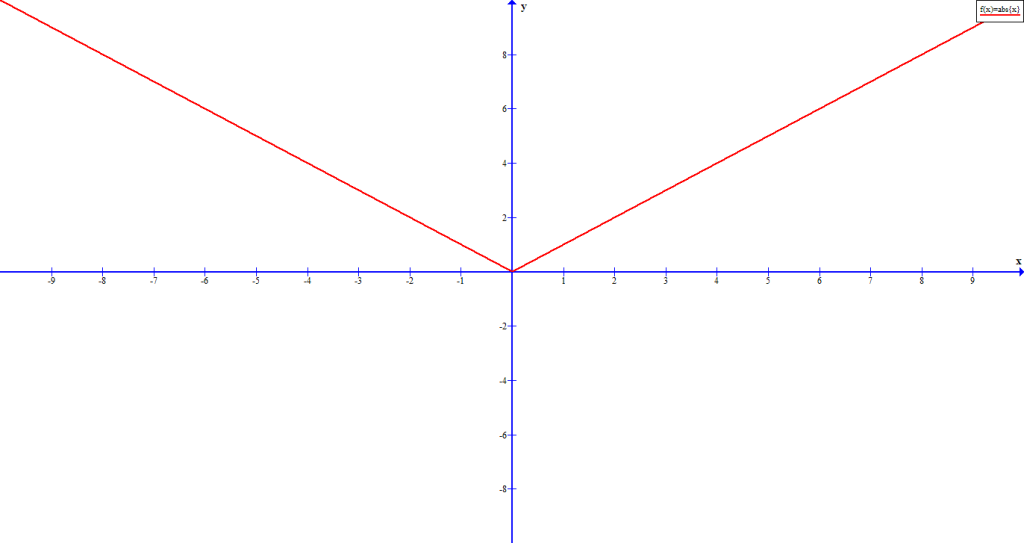
You can recognize the graph of a polynomial just by looking at the smoothness and continuity. Any sharp corner in graph is not a polynomial function.
End Behavior of Polynomial Functions
If you notice that the graph of polynomial has two ends – rightmost end and leftmost end. The end behavior depends on what kind of polynomial we are dealing with. The graph may go up or down during intervals, but the ends behavior depends of a polynomial ![]() depends on
depends on
- coefficient
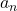 of the leading term
of the leading term 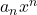 in the polynomial.
in the polynomial. - value of exponent
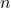 in the leading term
in the leading term 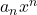 .
.
You can see from the figure 2, that when the value of variable ![]() increases, only leading term dominates , all smaller terms are insignificant. Therefore, we perform a leading coefficient test to determine the end behavior of the polynomial function.
increases, only leading term dominates , all smaller terms are insignificant. Therefore, we perform a leading coefficient test to determine the end behavior of the polynomial function.
When ![]() is odd:
is odd:
| left end decreases | right end increases | |
| left end increases | right end decreases |
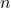 value and positive
value and positive 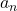 value.
value. 
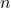 value and negative
value and negative 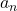 value.
value.When ![]() is even:
is even:
| left end increases | right end increases | |
| left end decreases | right end decreases |
The even polynomial has both ends pointing to same direction.
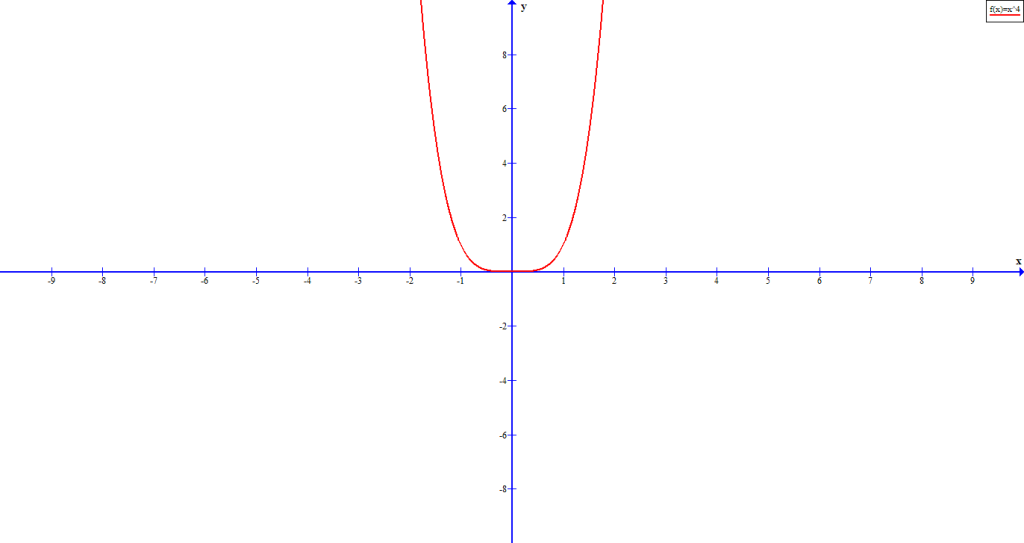
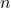 and positive
and positive 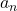 value
value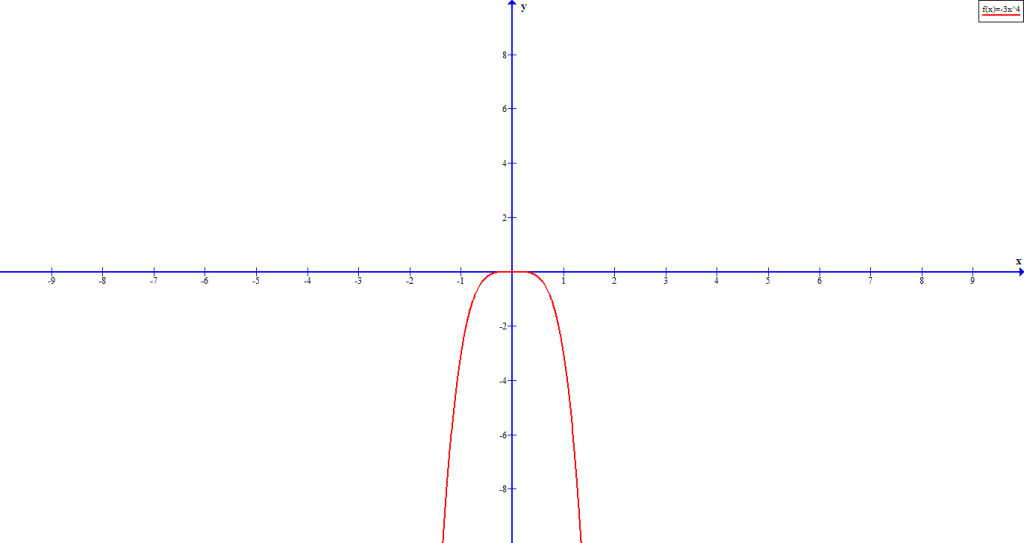
 and negative
and negative 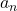 value
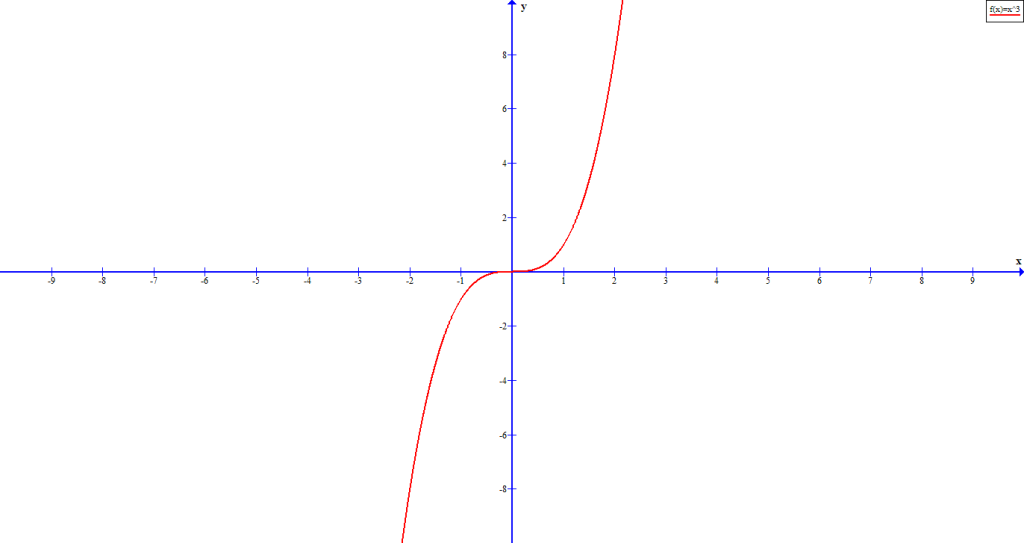
valueFigure 6 is graph of ![]() and figure 7 is graph of
and figure 7 is graph of ![]() .
.
Example #8
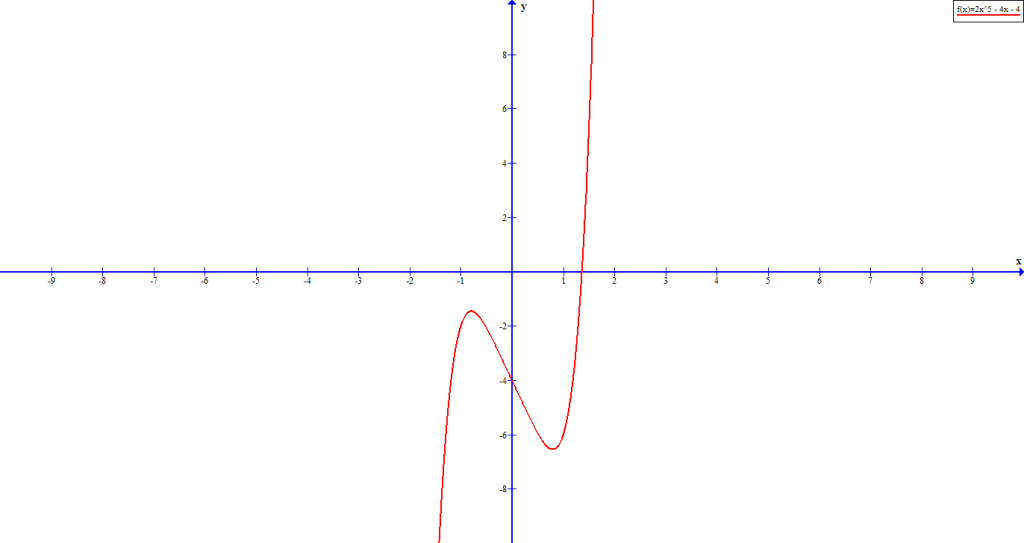
Determine the end behavior of the following function: ![]() .
.
Solution:
From the graph above it is easy to understand that this is an odd polynomial function with degree ![]() . The leading coefficient is
. The leading coefficient is ![]() which is greater than 0, that is,
which is greater than 0, that is, ![]() .
.
Therefore, the graph of has leftmost end decreasing and rightmost end increasing as variable ![]() increases without bound.
increases without bound.
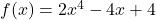
Zeros Of Polynomial Function
If ![]() is a polynomial function, then value of
is a polynomial function, then value of ![]() for which
for which ![]() is called zero of polynomials. There can be more than one zeros of a polynomial function.
is called zero of polynomials. There can be more than one zeros of a polynomial function.
The zeros of a polynomial function are called roots or solutions to the function ![]() . They appear as x-intercept in the graph of a polynomial function.
. They appear as x-intercept in the graph of a polynomial function.
Example #8
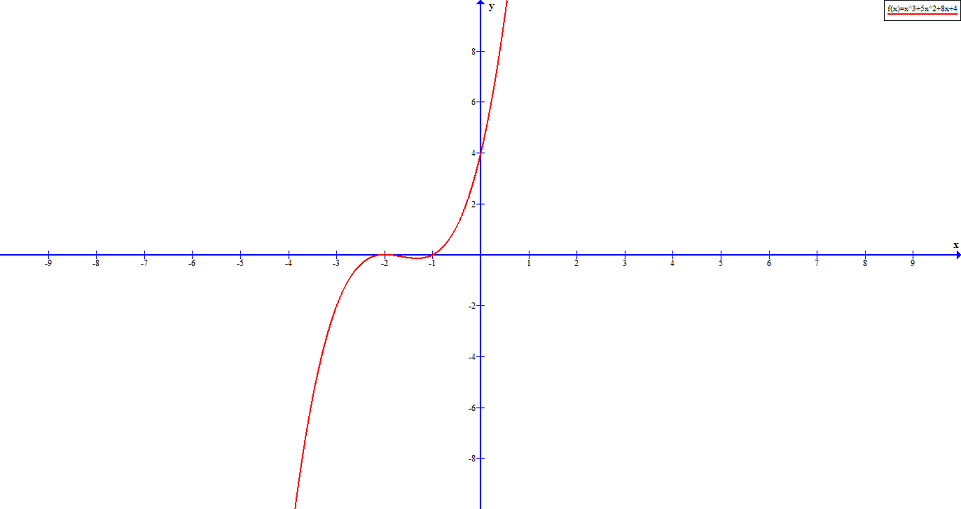
Find the zeros of the polynomial: ![]() .
.
Solution:
This problem cannot be solved with grouping technique. So checking whether ![]() is a solution.
is a solution.
![]()
Therefore, ![]() is a solution.
is a solution.
Using ![]() we can perform a polynomial division to find the roots.
we can perform a polynomial division to find the roots.
\begin{aligned}
&\frac{x^3 +5x^2 + 8x + 4}{x + 1} = x^2 + 4x + 4 = (x + 2)^2
\end{aligned}Therefore, the roots are ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
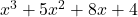 is at
is at 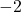 and
and
Multiplicities of the Root
In the above example, the root ![]() is repeated two times and not crossing the x-axis The graph shows that root
is repeated two times and not crossing the x-axis The graph shows that root ![]() which crosses the x-axis. This is called multiplicity of the root.
which crosses the x-axis. This is called multiplicity of the root.
- If the multiplicity of the root is even, that means if the root repeat itself even times, it does not cross the x-axis.
- If the multiplicity of the root is odd, then the root cross the x-axis.
The reason why graph does not cross the x-axis when the multiplicity is even is because when the multiciplity is even, the sign of the ![]() does not change at all.
does not change at all.
Example #9
Consider the following graph of ![]() which has two roots
which has two roots ![]() and
and ![]() . The factors of the function are
. The factors of the function are ![]() .
.
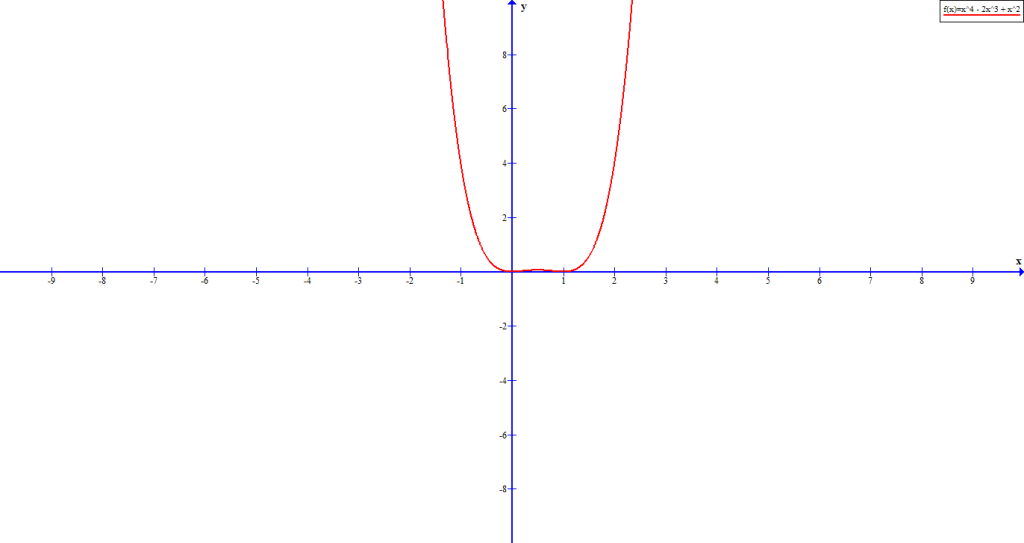
The graph clearly shows that the function does not cross the the x-axis at ![]() or
or ![]() .
.
Example #10
In this example, we have a polynomial function : ![]() whose factor is
whose factor is ![]() . The x-intercept is
. The x-intercept is ![]() .
.
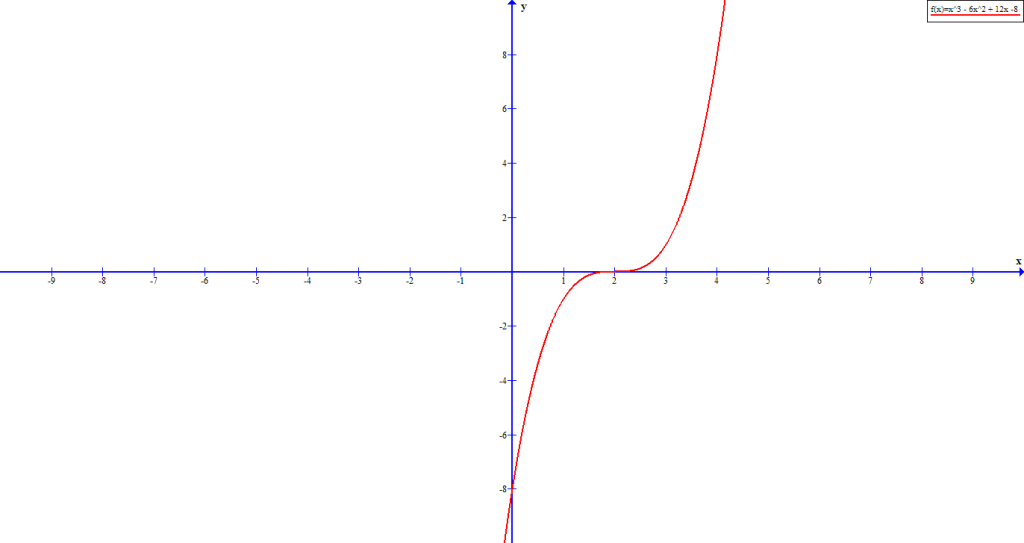
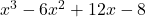
The graph crosses the x-axis at ![]() because the multiplicity of the root is odd.
because the multiplicity of the root is odd.