Limits and continuity of function is where calculus topics starts, however, to know calculus you must complete all lessons of pre- calculus with examples.
Limit of a function is a certain value that a function approaches, whereas a function is said to be continuous when the function has no breaks or drawn without taking the pen away from the paper.
How to understand a limit of a function?
Limit of a function is a certain value on x- axis that a function of x approaches from both the sides. When a function of x approaches to n (where n is an integer), then all the values of x are very close to n from both the side of the number line. For example, when function of x approaches to 2, then the the values near to the limit of a function from the left if 1.9, 1.99, 1.999 etc. and from the right is 2.1, 2.01, 2.001 etc.
Limit with an example
Let us say is a function whose limit is 2, then, the limit of a function can be written as
. This can be showed in the form of a graph.
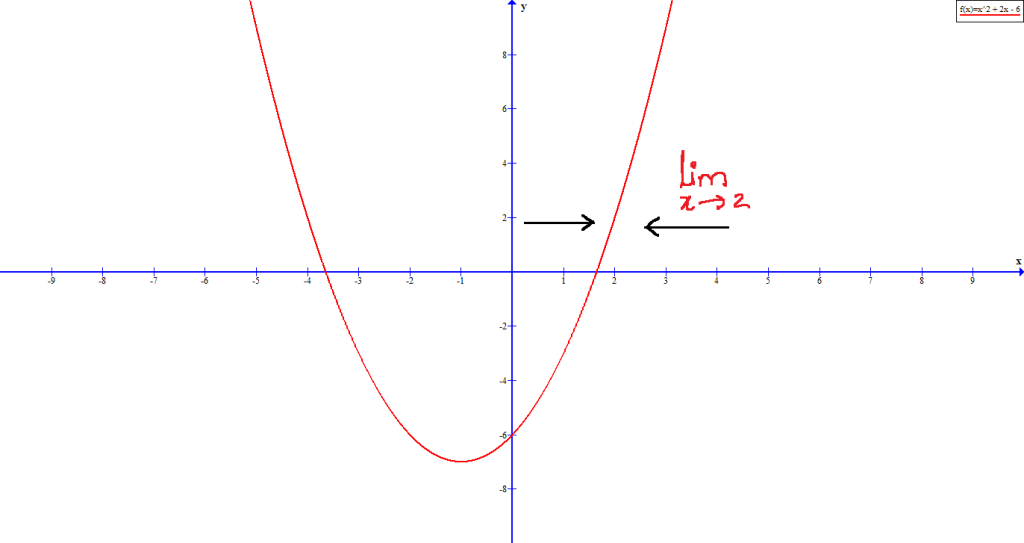
While finding the limit of a function, what should we observe?
Finding the limit of a function is all about observing the particular value a function approaches from left and right. From figure 1, it can be observed that both the right hand limit and left hand limit of a function approaches to the same number. In the above graph, the limit approaches from both right and left to 2.
means that x approaches c from left and reach all numbers smaller than c.
Similarly, means that x approaches c from right and reach all numbers greater than c.
Note: the value of x is never equal to c.
Continuity of a function
The limits applies to a continuous function. If the function is continuous, then a limit exists, otherwise not.
What is continuity of a given function?
A function is said to be continuous, when graph for the given function shows no breaks or discontinuity at a point or at least in a given interval.
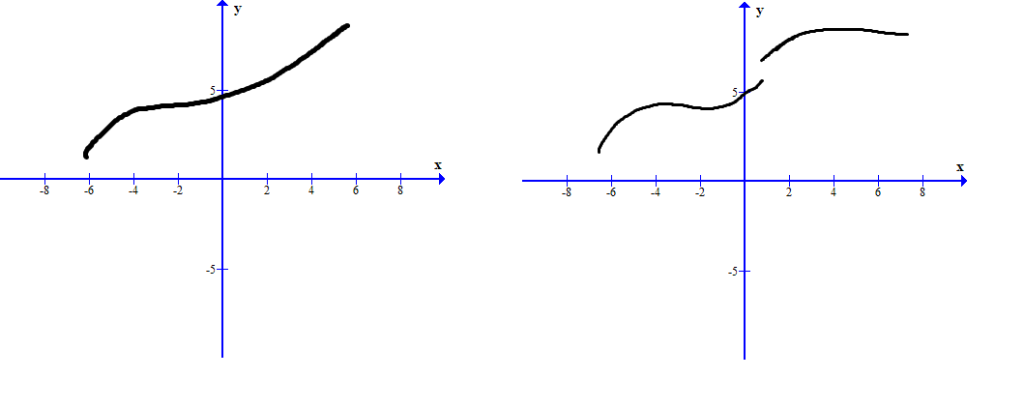
How to find whether a function is continuous?
Continuity of a function can be examined in two ways.
- Continuity of a function at a given point
- Continuity over a given interval
For finding the continuity of is given function is, the given function should have no breaks at the neighbourhood to a given point.
How to determine the continuity of a function at a given point?
For checking the continuity of a function at a given point, then it must satisfy the following conditions viz.,
- The point at which continuity of a function is examined should be within the domain of the function.
- Both the left handed and right handed limit of the function approaching to the point should be equal.
Summary
- Limit of a function is approached from both the sides.
- If the difference between the nearest value and the limit n is
etc., then the values approaching from the left is
.
- In the same case, the values approaching from the right is
.
- Continuity is defined as a function without any breaks or jumps.